Windows Server comes in two main installation types: Server Core and Server Standard (Desktop Experience). Both offer powerful server features, but they differ in usability, performance, security, and management approach.
In this guide, we’ll break down the differences, compare advantages, and help you decide which option is best for your environment.
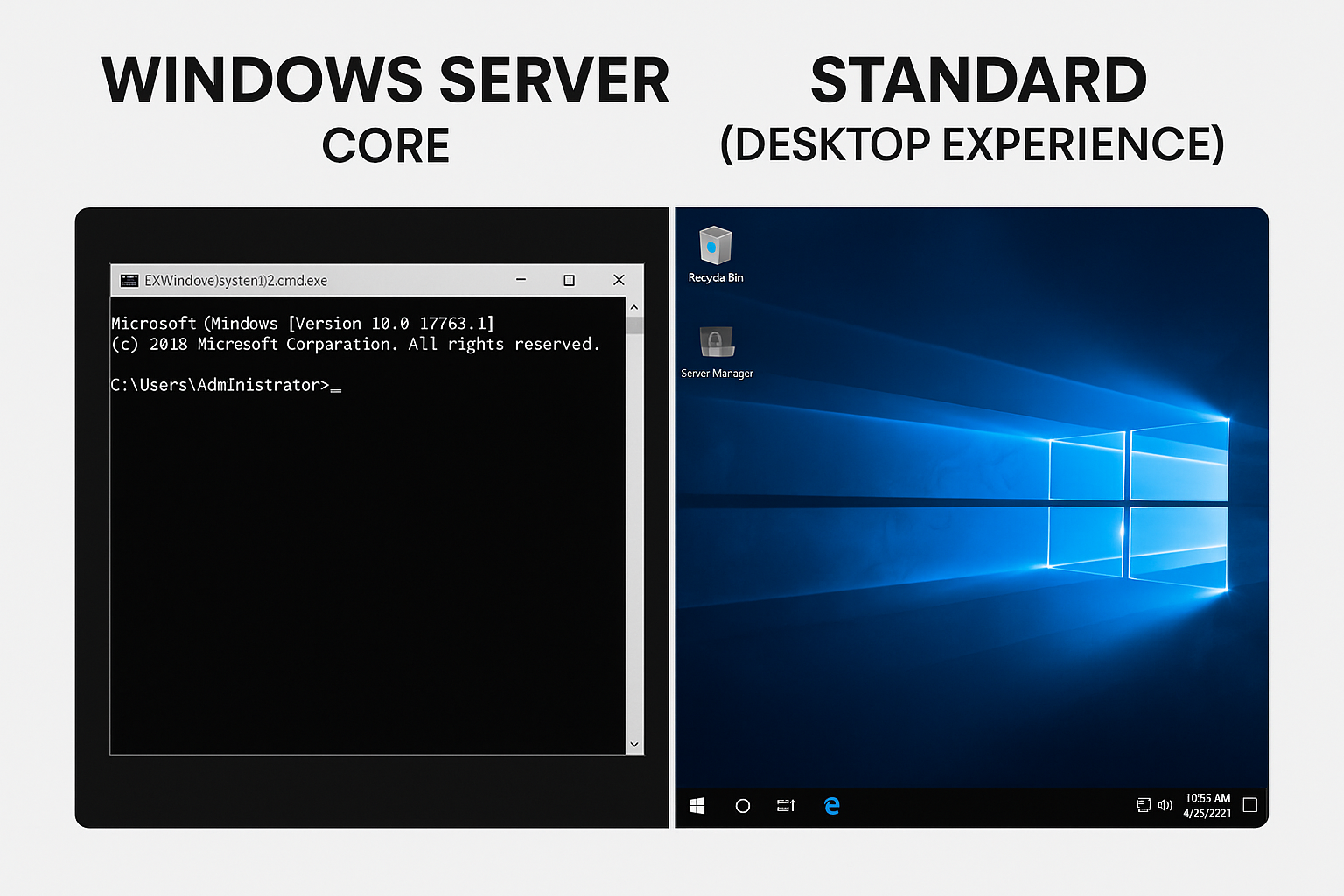
🖥️ What is Windows Server Core?
Windows Server Core is a minimal installation option without a graphical desktop environment.
It has:
- No traditional desktop
- No Start Menu
- No GUI tools
- Only command-line tools (PowerShell, CMD, Sconfig)
Benefits
✔ Lower resource usage
✔ Smaller attack surface
✔ Faster installation
✔ Better performance
✔ Fewer updates required
Best for:
- Datacenter servers
- Virtual machines
- DC, DNS, DHCP servers
- Web servers
- Hyper-V
- Security-focused deployments
🪟 What is Windows Server Standard (Desktop Experience)?
Server Standard (Desktop Experience) includes the full Windows desktop GUI, similar to Windows 10/11 layout.
It contains:
- Full desktop graphical tools
- Explorer
- Server Manager
- Windows UI
Benefits
✔ Simple to manage
✔ Easy for GUI users
✔ Good for RDP administration
✔ Compatible with all server roles
Best for:
- Admins not comfortable with PowerShell
- General purpose servers
- File servers
- Backup servers
- Remote management via RDP
⚡ Core Differences (Quick Comparison)
| Feature | Server Core | Standard Desktop |
|---|---|---|
| GUI | ❌ No | ✅ Yes |
| Performance | ⭐ High | ⭐ Standard |
| Resource usage | Very low | Higher |
| Patching | Less frequent | More frequent |
| Security footprint | Very small | Medium |
| Admin experience | Advanced | Easy |
| Ideal for | Datacenters | Small/medium servers |
🛠 Management Options
Server Core
- PowerShell
- Sconfig
- Remote PowerShell
- Windows Admin Center (recommended!)
Standard Desktop
- GUI tools
- MMC
- Server Manager
- Control Panel
- File Explorer
🧠 Which one should you choose?
Choose Server Core if:
✔ you want maximum performance
✔ you prioritize security
✔ you’re running in datacenter/VM
✔ you’re comfortable with PowerShell
Choose Desktop Experience if:
✔ you need GUI tools
✔ you’re new to Windows Server
✔ you manage via RDP
✔ you have mixed IT skills in the team
💡 Example Usage Scenarios
Server Core
- Active Directory Domain Controller
- DNS/DHCP
- Hyper-V
- IIS
- RDS licensing server
Standard Desktop
- File server
- Print server
- Small business server
- Backup server
- Application server
🧾 Conclusion
Both Windows Server Core and Desktop Experience are powerful but for different purposes. Core focuses on performance and security, while Desktop Experience gives ease of management.
For modern enterprise and virtualized deployments, Server Core is increasingly the recommended option—especially when combined with Windows Admin Center.
Windows Server Core vs Standard (Desktop Experience) (F.A.Q)
Can you install GUI later on Server Core?
No — switching requires reinstalling the OS.
Does Server Core support Active Directory?
Yes, fully supported.
Can I manage Server Core remotely?
Yes — PowerShell, RSAT, Windows Admin Center.
0 Comments